Dewar vessels
Variants
Dewar vessels made of glass
All Dewar vessels manufactured by KGW-ISOTHERM are made of borosilicate glass 3.3 DIN/ISO 3585 (DWK or Schott Tubing). They are manufactured in accordance with the “Pressure Equipment Directive”, Directive 97/23 EC, (N4 with Appendix 1) and DIN EN ISO 16496 “Appliances with vacuum insulation”.
Structure and function of a glass Dewar flask
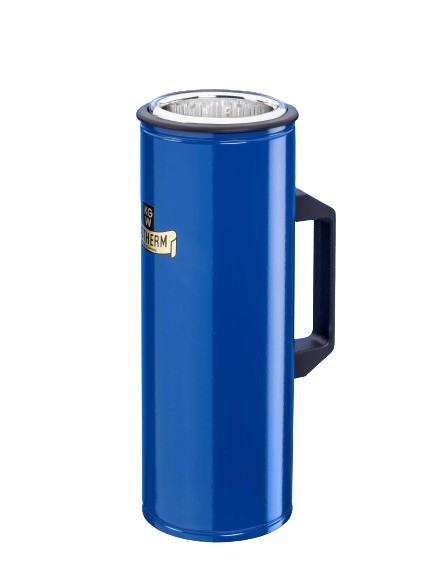
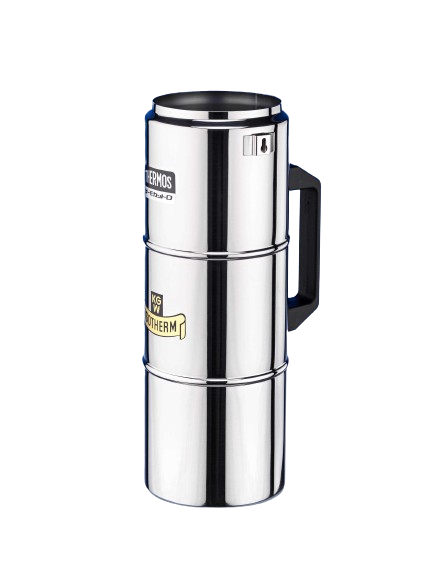
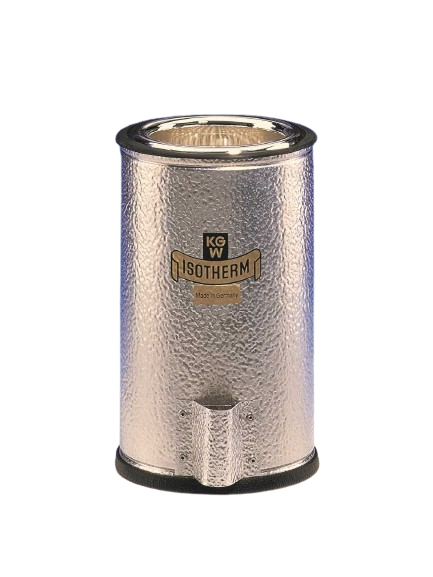
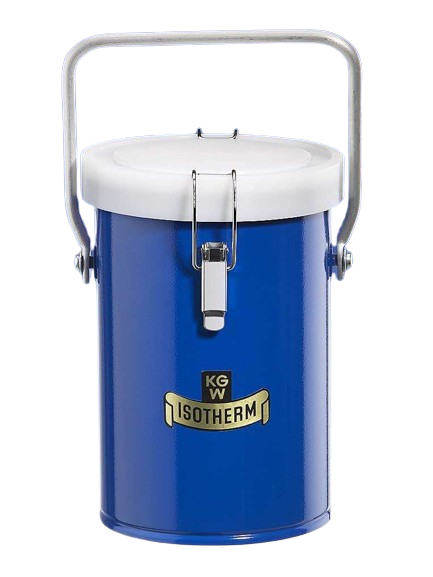
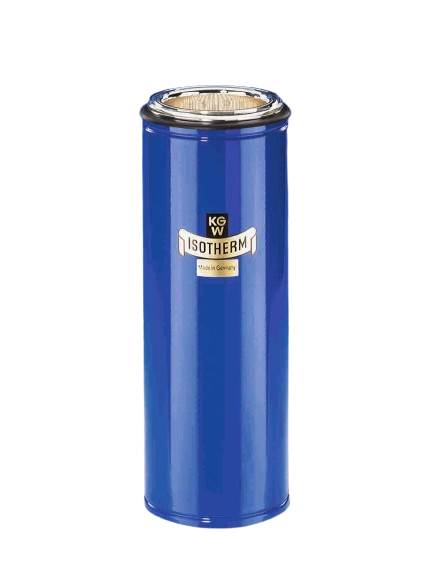
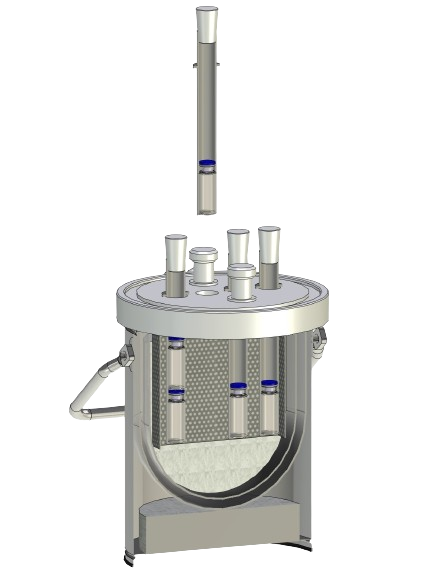
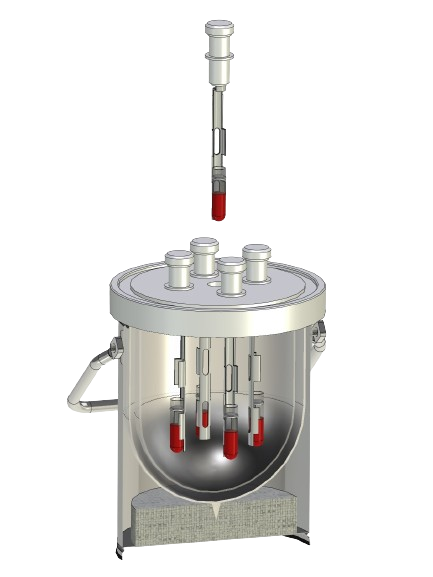
Dewar flasks made of glass are double-walled vacuum-insulated containers. They have the task of thermally insulating a product (LN2, CO2 or other coolant) stored in them against the ambient temperature. Dewar vessels consist of an inner and an outer flask, which are fused together at the top of the neck opening. The space between the inner and outer flask is vacuum-insulated to prevent heat contact between the product stored in the Dewar flask and the ambient temperature (contact heat). In addition, Dewar vessels made of glass have a silver coating in the vacuum chamber to minimize heat radiation. Optimum insulation is achieved by reducing both contact heat (vacuum) and radiant heat (mirror coating).
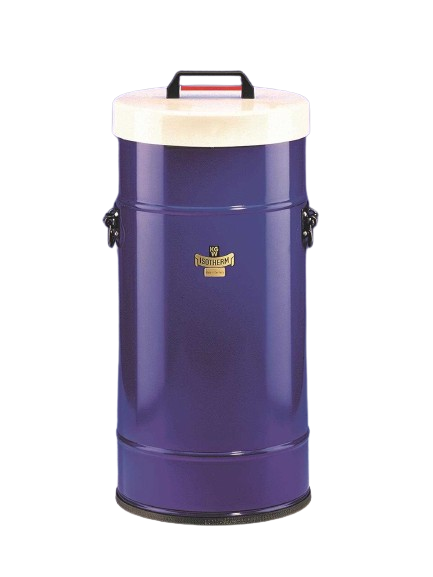
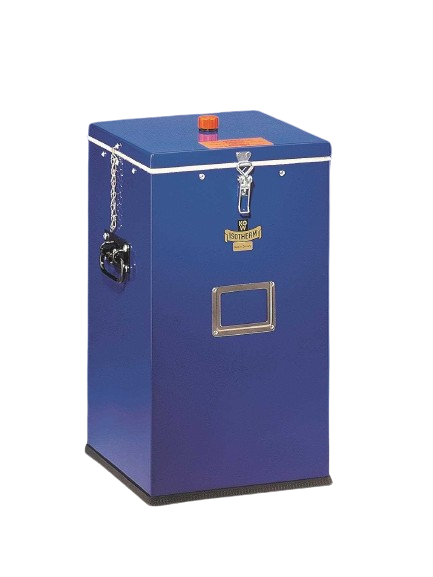
For safety and occupational safety reasons, the glass Dewar flasks must always be installed in a protective casing. This protective coating can be made of sheet metal, aluminum, stainless steel or a transparent PU coating.
All standard glass Dewar flasks may only be used up to a maximum overpressure of 0.1 bar. Higher working pressures on request.
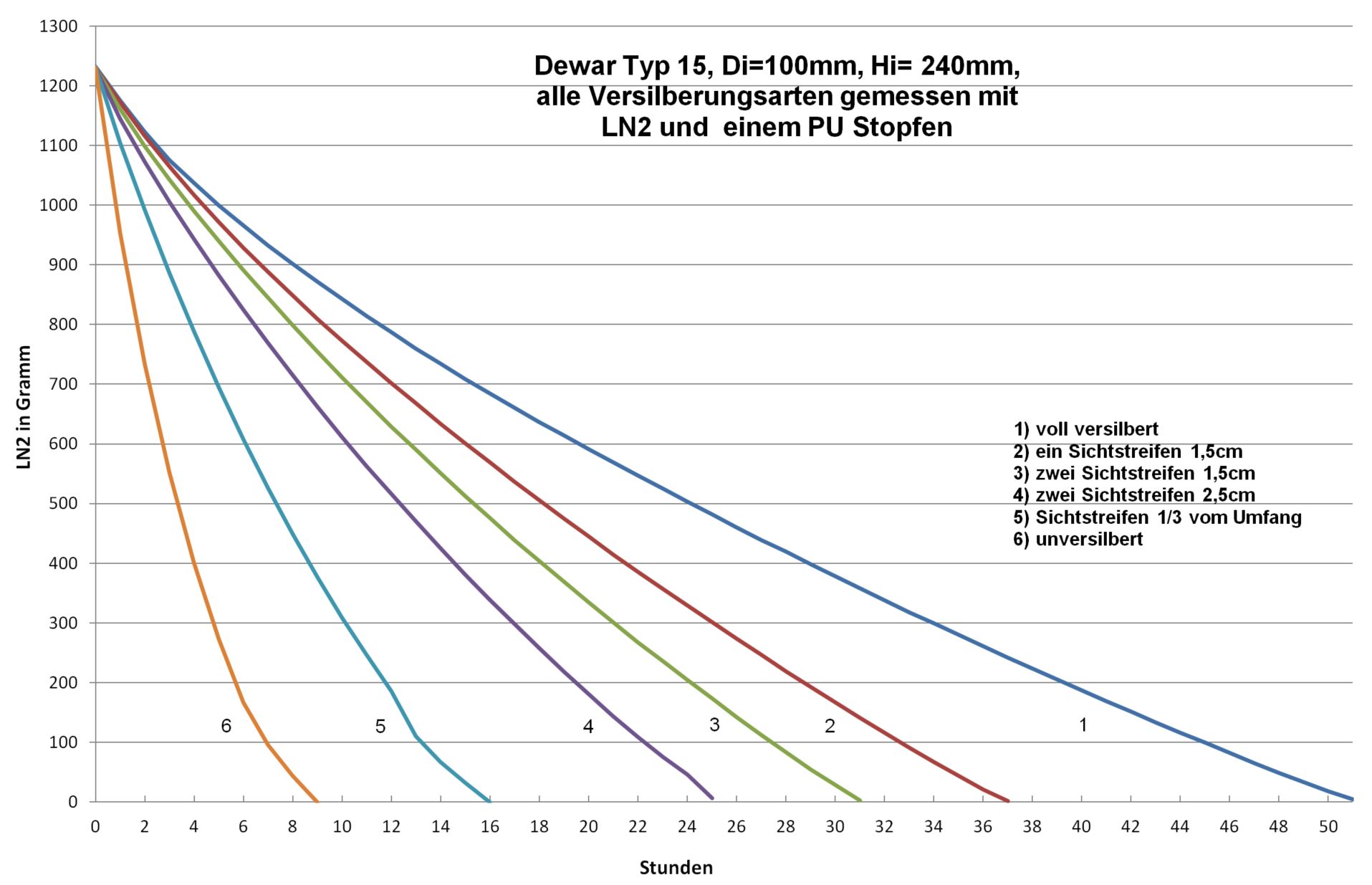
Types of silver plating and their influence on evaporation rates
Dewar flasks made of glass are double-walled vacuum-insulated containers. They have the task of thermally insulating a product (LN2, CO2 or other coolant) stored in them against the ambient temperature. Dewar vessels consist of an inner and an outer flask, which are fused together at the top of the neck opening. The space between the inner and outer flask is vacuum-insulated to prevent heat contact between the product stored in the Dewar flask and the ambient temperature (contact heat). In addition, Dewar vessels made of glass have a silver coating in the vacuum chamber to minimize heat radiation. Optimum insulation is achieved by reducing both contact heat (vacuum) and radiant heat (mirror coating).
For safety and occupational safety reasons, the glass Dewar flasks must always be installed in a protective casing. This protective coating can be made of sheet metal, aluminum, stainless steel or a transparent PU coating.
All standard glass Dewar flasks may only be used up to a maximum overpressure of 0.1 bar. Higher working pressures on request.